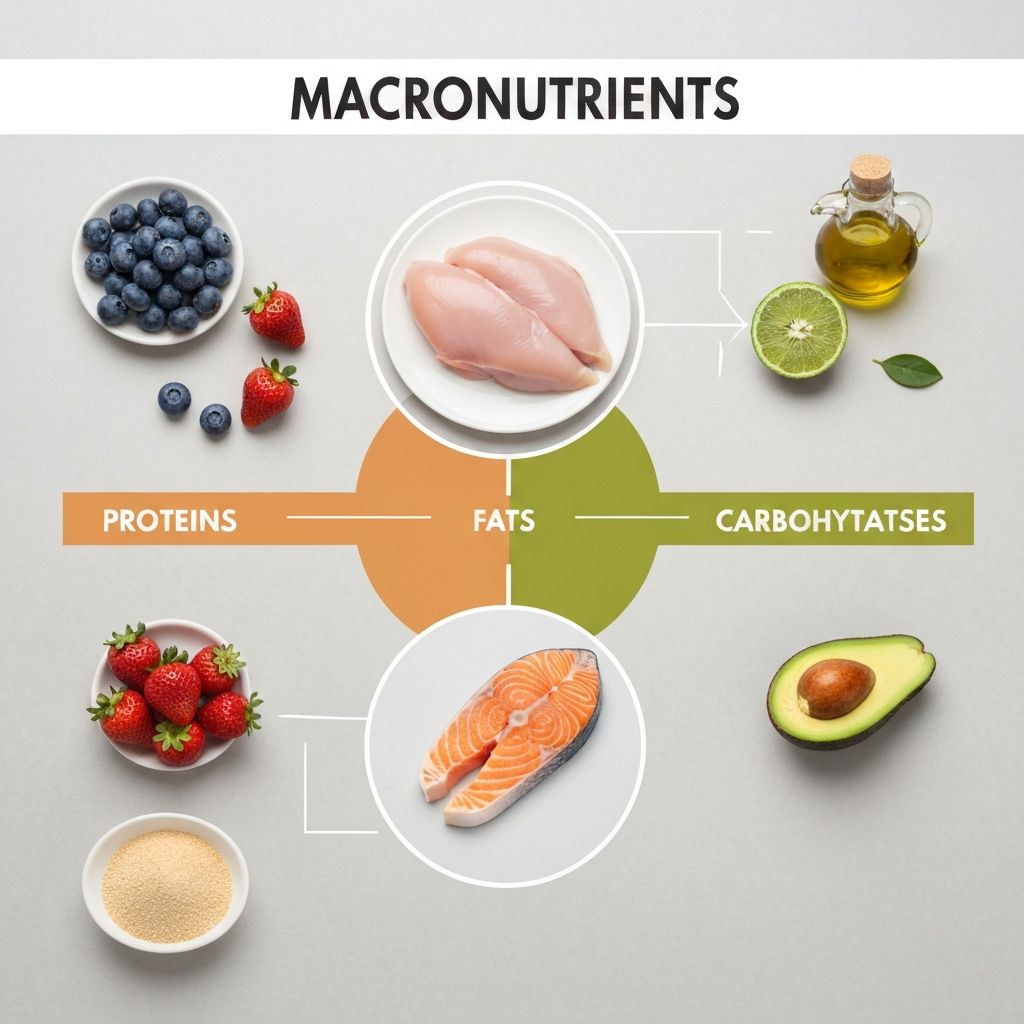
Introduction to Macronutrients
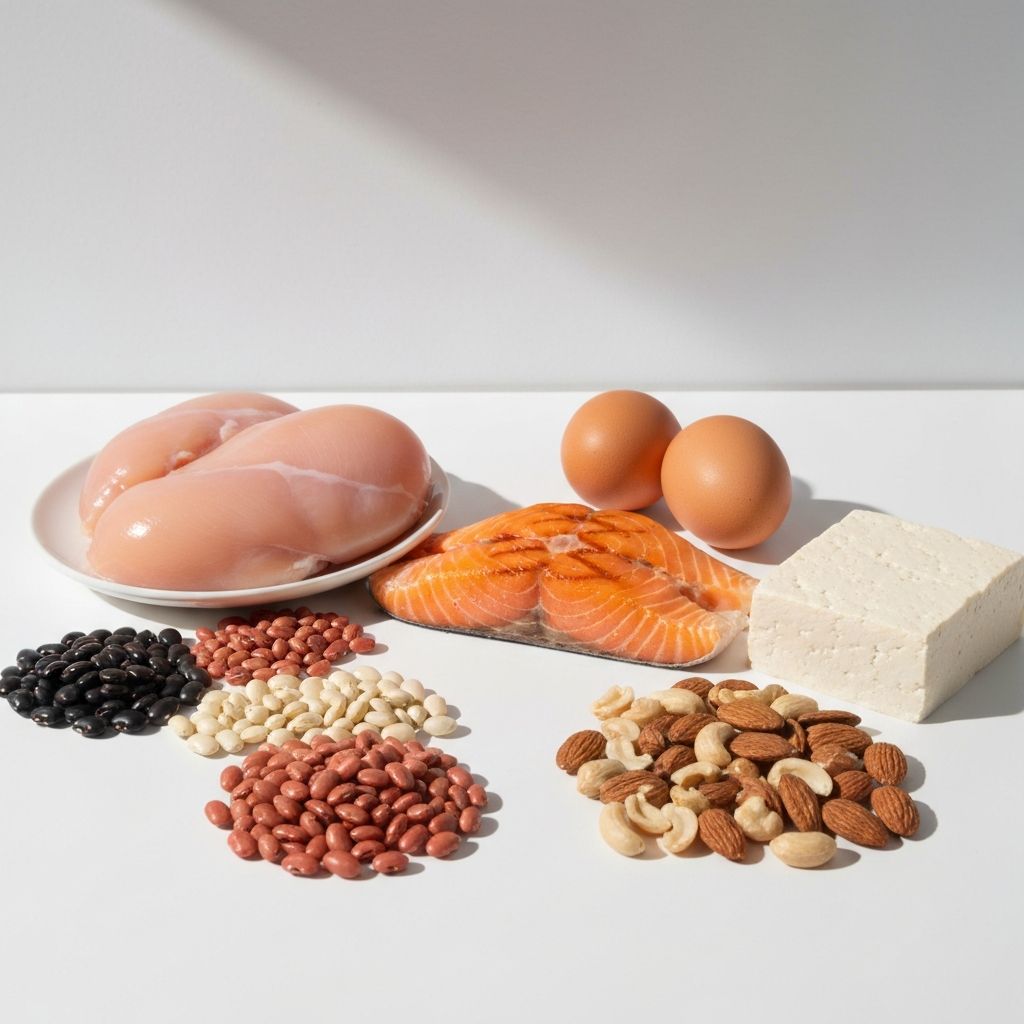
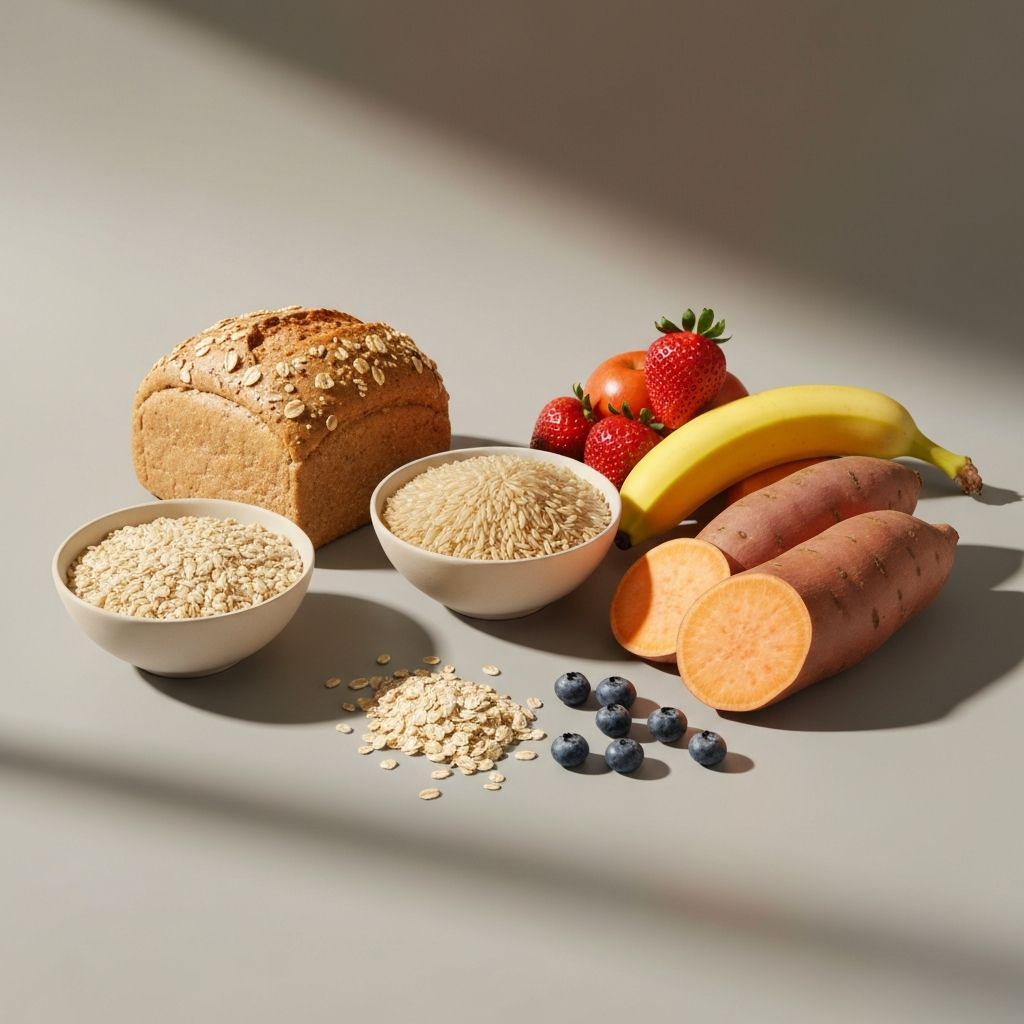
Macronutrients are the three main categories of nutrients that provide energy and support various bodily functions. These include proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Each plays a distinct role in maintaining overall health and wellbeing.
This educational resource explores how these macronutrients function in the human body, their various sources, and their general significance in daily nutrition. The information presented here is for educational purposes only and does not constitute personalised dietary advice.